Indirect Dynamic Free Cooling from STULZ is the only system worldwide with automatic efficiency optimization. Dynamic switching operation and control without a fixed free cooling start value and an additional operating mode guarantee maximum savings potential.
The Free Cooling system with dynamic switching operation and control
In classic precision cooling, the necessary cold is created independently of the outside temperature by means of mechanical cooling. The most energy-intensive component here is the compressor.
To reduce mechanical cooling to a minimum, STULZ developed a Free Cooling system with dynamic switching operation and control for in-house units. This controls all active components, dependent on the outside air temperature and current heat load.
Benefits of the dynamic switching operation and control at a glance
- Minimal compressor running time
- Switching operation and control according to actual heat load
- Maximized periods of Free Cooling
- Automatic selection of the optimum operating mode without a fixed Free Cooling start value
- Minimized operating costs
Reduction of energy consumption by up to 60%
The dynamic switching operation and control reduces the compressor running time to a minimum and reduces the total energy consumption by up to 60%, taking into account all active components.
The system cools precisely and dynamically according to the current heat load. This means that only the required cooling capacity is ever generated and there is no energy-intensive oversupply. Taking into consideration outside temperature and current heat load, the dynamic switching operation and control selects the optimum operating mode without a fixed Free Cooling start value.
If the outside air temperature is 3 Kelvin under the return air, the outside air can even be used for cooling. The Free Cooling periods are maximized by the dynamic switching operation and control and extended Free Cooling, reducing operating costs to a minimum.
More Free Cooling, fewer costs
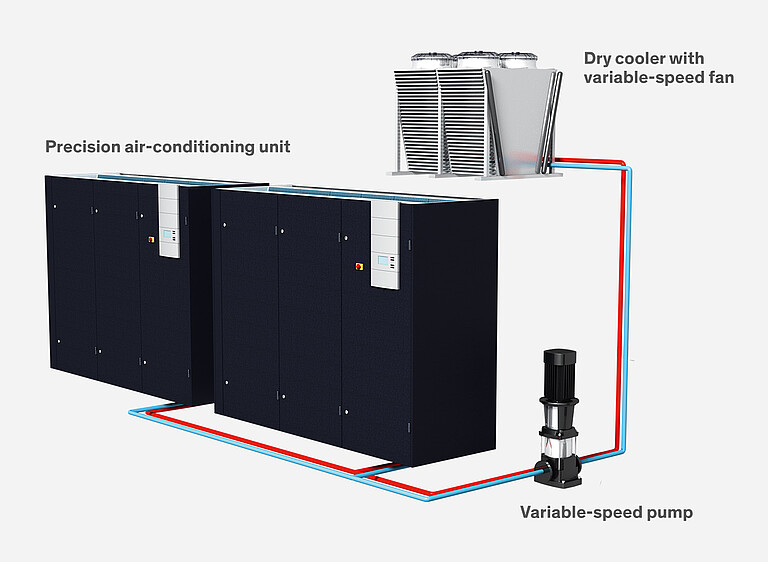
To further extend the Free Cooling operation and thereby drastically reduce operating costs, the dynamic switching operation and control has another operating mode: Extended Free Cooling
In the Extended Free Cooling operating mode, the use of variable-speed pumps and dry coolers with fan speed control maintains the cooling capacity by increasing the airflow. This means the Free Cooling operation is also extended and the operating costs are reduced to an absolute minimum.
Operating modes
Free Cooling
Compressor: Off | Fan: Set point | CRAC: |
Standby unit: On | Pumps: Variable | Dry cooler fans: |
Extended Free Cooling
Compressor: Off | Fan: Max. | CRAC: |
Standby unit: On | Pumps: Max. | Dry cooler fans: |
Mixed mode
Compressor: Variable | Fan: Set point | CRAC: |
Standby unit: On | Pumps: Max. | Dry cooler fans: |
Compressor mode
Compressor: On | Fan: Set point | CRAC: |
Standby unit: Off | Pumps: Min. | Dry cooler fans: |
Standby management for even more efficiency
To ensure the greatest possible safety in air conditioning, redundancies are often created in the air conditioning units. This means that more units are installedthan are actually required for air conditioning.
With the usual passive redundancy, these units are only (automatically) put into operation when a running device switches off due to an error.
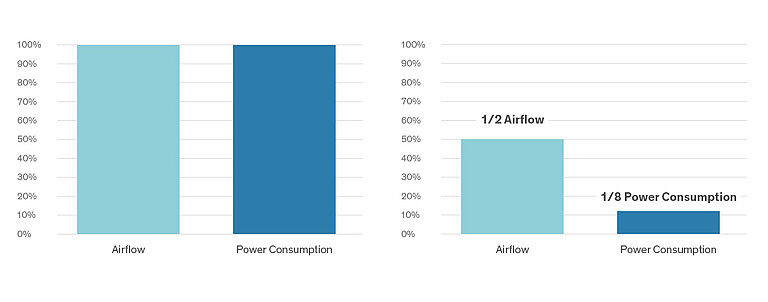
The dynamic switching operation and control enables the use of standby units with the greatest efficiency possible. With the active redundancy used for this, all installed units are in operation – even the standby units.
The potential of the EC fans is fully utilized: All units are operated with an airflow which is the same overall, but reduced for each unit. The reduced airflow means that the power consumption of the fans and the related operating costs are reduced even further.